Implementation of Simply Linked Lists in C++
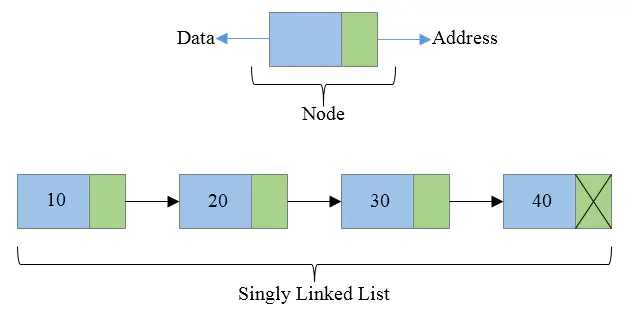
The aim of the project
Write a computer program containing
- Description of the structure containing fields such as string, int, double;
- a set of functions to work with the list based on this structure:
- Add an item to the top of the list;
- Add an element to the end of the list;
- Add an element to the list after the specified element;
- Add an item to the list before a given item;
- Remove an item with a specified name from the list;
- Display list contents on the screen; is a main function that contains a list script that uses the developed toolkit.
Project preview
In this project, I created a simple-linked list, each node of which stores the data of a certain person: name, height and weight. The set of functions specified in the project objectives was realized.
The whole project can be seen in the very near future HERE.
How did I do it anyway?
- We declare the structure of the node containing 3 fields (string, int, double) and a reference to the next element.
struct Human {
string name;
int growth;
double weight;
Human* next;
};
- We can add an item to the top of the list. We transmit the link to the pointer of the first element and the field of our structure (hereinafter «basic parameters»). Create a new object of type Human, its address is assigned to the variable (newNode) Then “put” into the function basic parameters passed to functions. Set the new node link to the list’s head (pNode) and set the new node as the list head.
void AddFirst(Human* &pNode, string name, int growth, double weight) {
Human* newNode = new Human;
newNode->name = name;
newNode->growth = growth;
newNode->weight = weight;
newNode->next = pNode;
pNode=newNode;
}
- We implement the function of adding an element to the end of the list. We pass the reference to the pointer of the first element and basic parameters. Create a new object of type Human, its address is assigned variable (newNode). Next, “put” in the function basic parameters and set the link of the new node to the list’s head (pNode). If we have an empty list, we essentially create the 1st element. Else we look for the last element, then put the tmp address of the last element of the list.
void AddLast(Human* &pNode, string name, int growth, double weight) {
Human* newNode = new Human;
newNode->name = name;
newNode->growth = growth;
newNode->weight = weight;
newNode->next = pNode;
if (pNode == nullptr) {
newNode->next = nullptr;
pNode = newNode;
}
else {
Human* tmp = pNode;
while (tmp->next != nullptr)
tmp = tmp->next;
newNode->next = nullptr;
tmp->next=newNode;
}
}
- We can add an element after the specified element. Pass the pointer to the first element to copy the external object (pNode), the string on which the node will be searched and the basic parameters. If we have an empty list, we will display a message about it. We are looking for the element we need, i.e. we set the top of the list and move on the list. If you have reached the last element and have not found the desired one, we will display the corresponding message.
void AddAfter (Human* pNode, string Node, string name, int growth, double weight) {
if (pNode == nullptr) {
cout << "This list is empty\n";
return;
}
Human* tmp = pNode;
while (tmp->next != nullptr and tmp->name != Node)
tmp = tmp->next;
if (tmp->next == nullptr and tmp->name != Node) {
cout << "No element in the list\n";
return;
}
Human* newNode = new Human;
newNode->name = name;
newNode->growth = growth;
newNode->weight = weight;
newNode->next = pNode->next;
pNode->next = newNode;
}
- We can add an element before the specified one. Pass the pointer to the first element to copy the external object (pNode), the string on which the node will be searched and the basic parameters. If we have an empty list, we will display a message about this. If the first element is the search element, we call the AddFirst function. Create variables that store references to previous (prev) and subsequent (tmp) elements. Then cycle to find the desired node (Node). If you have reached the last element and have not found the desired one, we will display the corresponding message. If found, we perform standard actions by filling the new node and setting the next field to tmp, and the next y prev field installs to the newly created node.
void AddBefore(Human* pNode, string Node, string name, int growth, double weight) {
if (pNode == nullptr) {
cout << "This list is empty\n";
return;
}
if (pNode->name == Node) {
AddFirst(pNode, name, growth, weight);
return;
}
Human *prev = pNode, *tmp = pNode->next;
while (tmp->next != nullptr and tmp->name != Node) {
tmp = tmp->next;
prev = prev->next;
}
if (tmp->next == nullptr and tmp->name != Node) {
cout << "No element in the list\n";
return;
}
Human* newNode = new Human;
newNode->name = name;
newNode->growth = growth;
newNode->weight = weight;
newNode->next = tmp;
prev->next = newNode;
}
- We implement the node deletion function by name (name). We pass the reference to the pointer of the first element and the string on which the node will be searched. If we have an empty list, we will display a message about it. Create a variable tmp, set it to the top of the list. If the first element of the list is the search element, then remove it and override pNode (pointer to the first element of the list). If we have an empty list, we will display a message about this. Create a prev variable and put pNode in it. In tmp we will pass pNode->next. Then search for the desired element. If you have reached the last element and have not found the desired one, print the corresponding message. If you find the element you are looking for, override prev->next and remove the element itself (tmp).
void Del(Human* &pNode, string Node) {
if(pNode == nullptr) {
cout << "List is empty\n";
return;
}
Human *tmp = pNode;
if(pNode->name == Node) {
pNode = pNode->next;
delete tmp;
return;
}
if (pNode->next == nullptr) {
cout << "No element in the list\n";
return;
}
Human *prev=pNode;
tmp = pNode->next;
while (tmp->next != nullptr and tmp->name != Node) {
tmp = tmp->next;
prev = prev->next;
}
if(tmp->next == nullptr and tmp->name != Node) {
cout << "No element in the list\n";
return;
}
if(tmp->name == Node) {
prev->next = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
return;
}
}
- We implement the function of displaying the list on the screen. As a parameter, we transmit the pointer to the first element. If we have an empty list, we will display a message about this. We will set tmp at the top of the list. Then we display the node data, we switch to the next element (tmp = tmp->next) and so until we reach the last element.
void Showmen(Human *pNode) {
if (pNode == nullptr) {
cout << "This list is empty\n";
return;
}
Human *tmp = pNode;
while(tmp != nullptr) {
cout<<"Name: " << tmp->name << "\nGrowth: " << tmp->growth << "\nWeight: " << tmp->weight << endl << endl;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
}
- In the main function, we implement a list scenario that uses the developed toolkit. Create list1 list. Next, the previously implemented functions are performed sequentially. Add to the beginning (“Tom”), add to the beginning (“Lisa”), add after Toma (“Fred “), add before Fred (“Jeff “), remove (“Lisa “), add to the end (“Mary “).
int main() {
Human* list1 = nullptr;
AddFirst(list1, "Tom", 175, 70.55);
Showmen(list1);
cout<<"-----------------------------------------------------------------------"<<endl << endl;
AddFirst(list1, "Lisa", 150, 59.64);
Showmen(list1);
cout<<"-----------------------------------------------------------------------"<<endl << endl;
AddAfter(list1, "Tom", "Fred", 189, 100.38);
Showmen(list1);
cout<<"-----------------------------------------------------------------------"<<endl << endl;
AddBefore(list1, "Fred", "Jeff", 140, 56.49);
Showmen(list1);
cout<<"-----------------------------------------------------------------------"<<endl << endl;
Del(list1, "Lisa");
Showmen(list1);
cout<<"-----------------------------------------------------------------------"<<endl << endl;
AddLast(list1, "Mary", 162, 51.26);
Showmen(list1);
cout<<"-----------------------------------------------------------------------"<<endl << endl;
return 0;
}
And in the end, I would like to remind you that the whole project can be seen in the very near future HERE.