External course. Cybersecurity basics

Aim of the work
Completion of external course control assignments “Cybersecurity basics”
How the internet works: basic network protocols
UDP - network layer protocol TCP - transport level protocol HTTPS - application level protocol IP - network layer protocol, therefore the response is HTTPS.
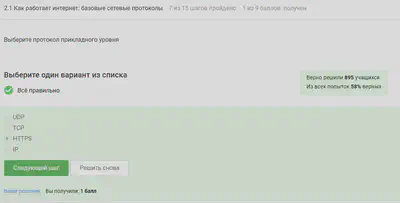
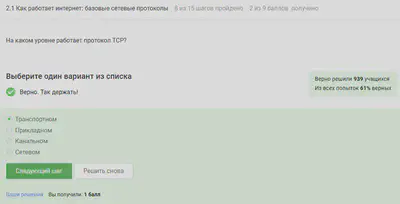
It was mentioned earlier that the TCP protocol - transmission control protocol - works at the transport level.
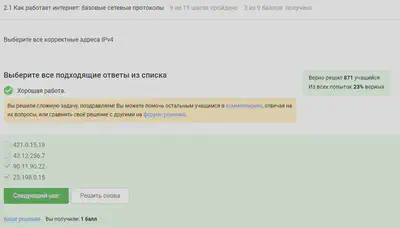
An IPv4 address cannot be more than 255, so the first two options are not suitable.
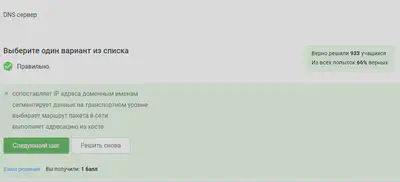
DNS server, Domain name server - application designed to answer DNS requests according to the appropriate protocol Mandatory condition - The server mapping of domain names to an IP address is called name and address resolution.
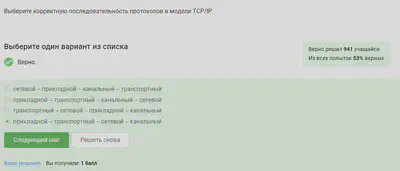
Distribution of protocols in TCP/IP models:
-
Application layer (HTTP, RTSP, FTP, DNS).
-
Transport layer (TCP, UDP, SCTP, DCCP).
-
Network (Interconnect) level (Network Layer): IP.
-
Network access level (Channel) (Link Layer): Ethernet, IEEE 802.11, WLAN, SLIP, Token Ring, ATM and MPLS.
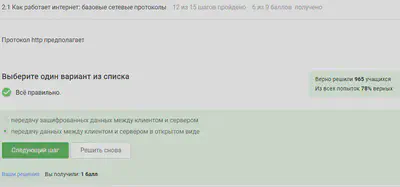
The http protocol does not transmit encrypted data, and the https protocol will already transmit encrypted data.
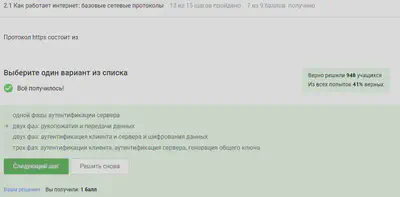
https transmits encrypted data, one phase is data transmission, the other should be a handshake.
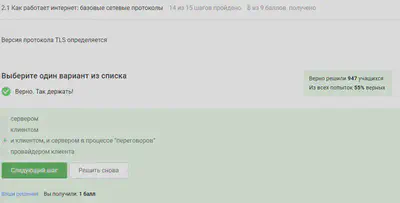
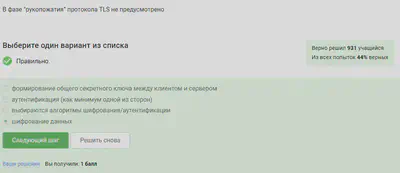
TLS is defined by both the client and the server to be able to connect.
The answer to the picture, the other options in the protocol are provided.
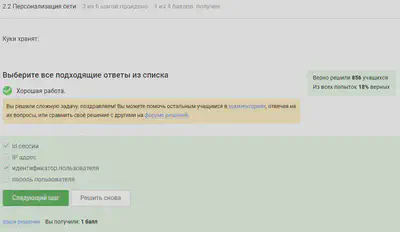
Network personalization
Cookies do not store passwords and IP addresses, but id ceccии and identifier are stored.
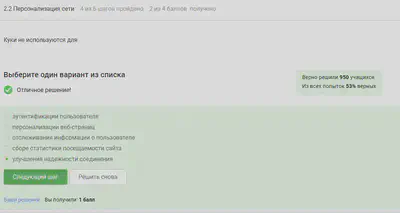
Of course, cookies do not make the connection more reliable.
The answer is in the image.
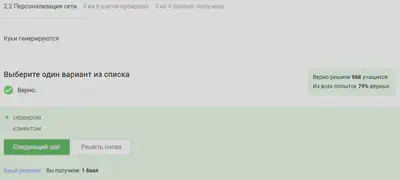
Session cookies are stored for the duration of the session, that is, while the website is in use.
There are three nodes - input, intermediate and output.
TOR Browser. Anonymization
The IP address should not be known to the security and intermediate nodes.
The sender generates a common secret key with nodes through which the transfer is going, that is to say with all.
You do not need to use TOR to receive packages. TOR is a technology that allows you to hide the identity of a person on the Internet with some success.
Wi-fi wireless networks
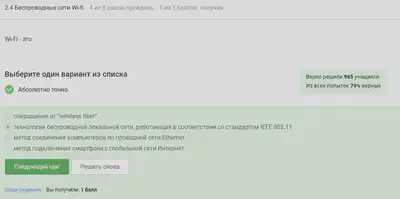
Indeed, this is the definition of WiFi.
For the purpose of working on the Internet, Wi-Fi is usually located as a channel level (equivalent to the physical and channel levels of the OSI model) below the Internet level of the Internet protocol. This means that the nodes have a linked Internet address, and if properly connected, it provides full access to the Internet.
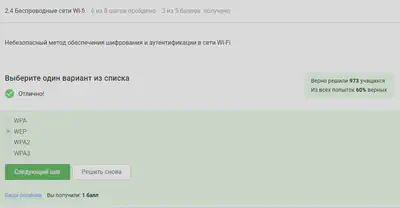
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is an outdated and insecure authentication method. It is the first and not a very successful protection method. Intruders without problems gain access to wireless networks that are protected with WEP, has been replaced by the others presented.
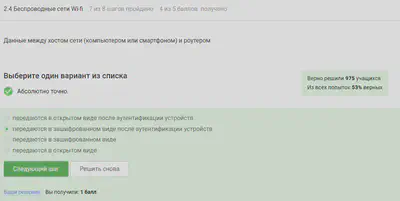
Need to authenticate the devices and later encrypted data is transmitted.
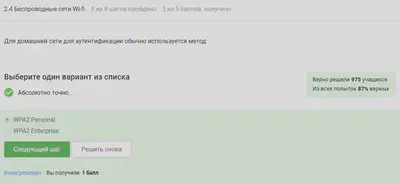
In general, it is clear from the name that WPA2 Personal for personal use, that is to say for home network, enterprise - for preferences.
Disk encryption
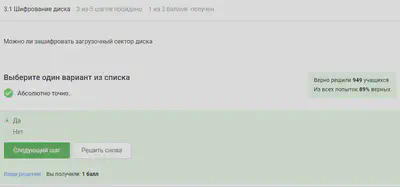
Disk encryption is an information protection technology that converts data on the disk into unreadable code. It is possible to encrypt the boot sector of the disk.
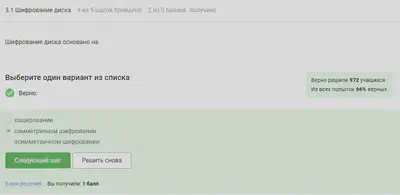
Disk encryption is based on symmetric encryption.
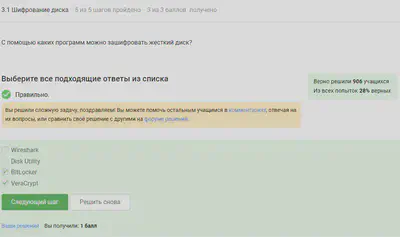
The programs with which it is possible to encrypt a disk are marked.
Passwords
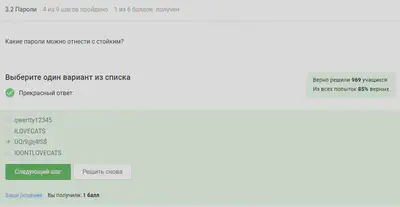
Strong password - the one that is more difficult to pick up, it should be with special. symbols and long.
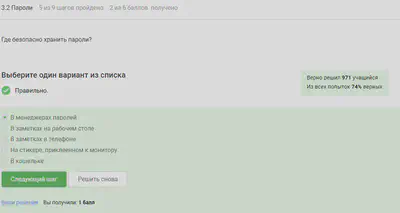
All options, except the password manager, are completely unreliable.
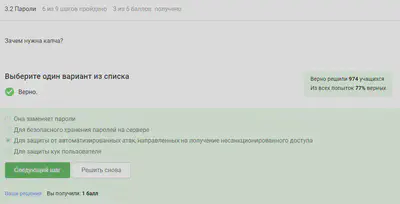
Kapcha is needed to check that behind the screen is “not a robot”.
It is dangerous to keep passwords in open form, so their hash is kept.
Salt won’t help.
All the above measures protect against data leakage.
Fishing
The phishing links are very similar to the links of known services, but with some differences.
Yes, maybe, for example, if the user has been hacked with a familiar address.
Viruses. Examples
Answer given according to definition.
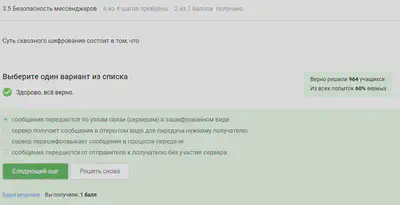
Security of messengers
When the first message is installed by the sender, the encryption key is generated.
The essence of end-to-end encryption is that messages are transmitted over nodes in encrypted form.
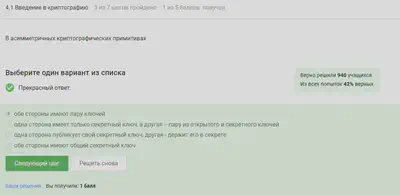
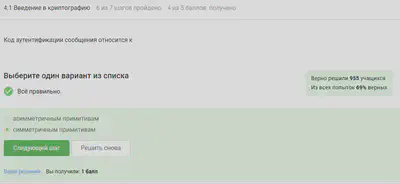
Introduction to cryptography
Asymmetric cryptographic systems imply that a pair of keys is on both sides.
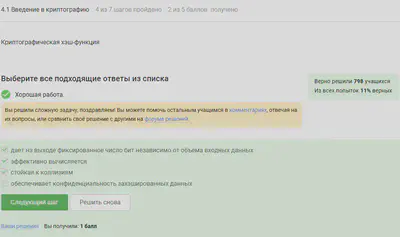
The basic conditions for cryptographic hash function have been noted.
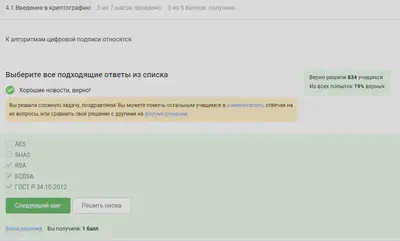
The algorithms of digital signature are marked.
In information security, message authentication or data source authentication is a property that ensures that the message has not been modified during transmission (data integrity) and that the recipient can verify the source of the message.
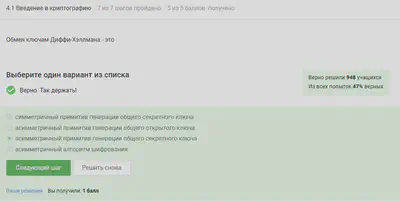
Diffie-Hellman key exchange definition.
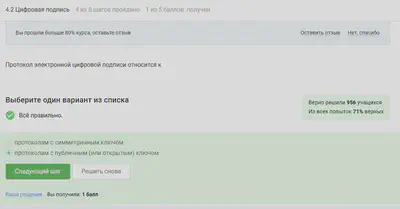
Digital signature
By definition, the digital signature of the EDP protocol refers to protocols with a public key.
The verification of an electronic signature is as follows. In the first step, the recipient of the message builds its own version of the signed document hash function. The second step is deciphering the hash function contained in the message using the sender’s public key. In the third step, two hash functions are compared. Their coincidence guarantees both the authenticity of the document content and its authorship.
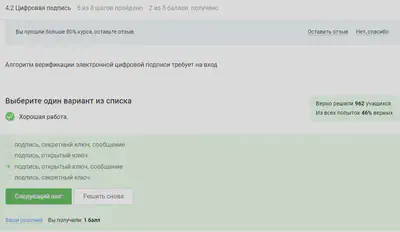
The electronic signature ensures all specified except confidentiality.
An enhanced qualified electronic signature is used to send tax returns to the FNS.
The correct answer is in the picture.
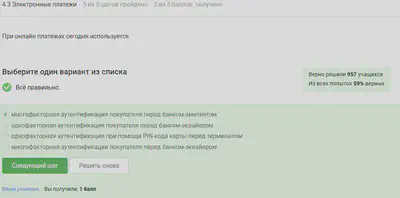
Electronic payments
Well-known payment systems - Visa, MasterCard, MIR.
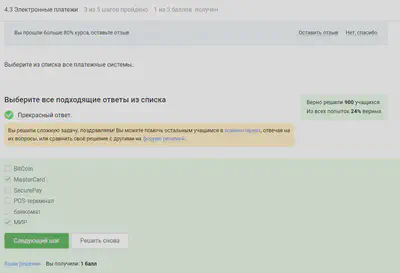
The correct answer to the picture.
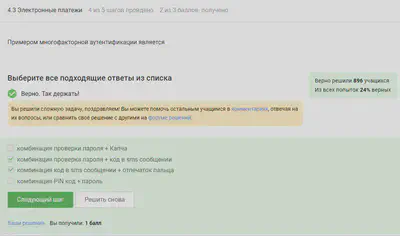
Multi-factor authentication is used for online payments.
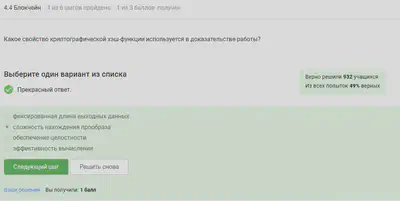
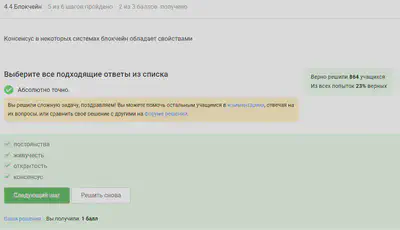
Blockchain
Proof-of-Work, or PoW (proof of performance) is a consensus algorithm in a blockchain; it is used to confirm transactions and create new blocks. With PoW, miners compete against each other for online transactions and rewards. Users of the network send each other digital tokens, after which all transactions are collected in blocks and recorded in a distributed registry, that is, in a blockchain.
Blockchain consensus is a procedure in which the network members agree on the current state of data in the network. This allows consensus algorithms to establish the reliability and credibility of the network’s identity.
The answer is a digital signature.
Conclusions
The course “Basics of cyber security” was completed. Knowledge obtained.
And at the end I would like to mention that the whole project can be seen HERE.
Course link: click